Air Monitoring
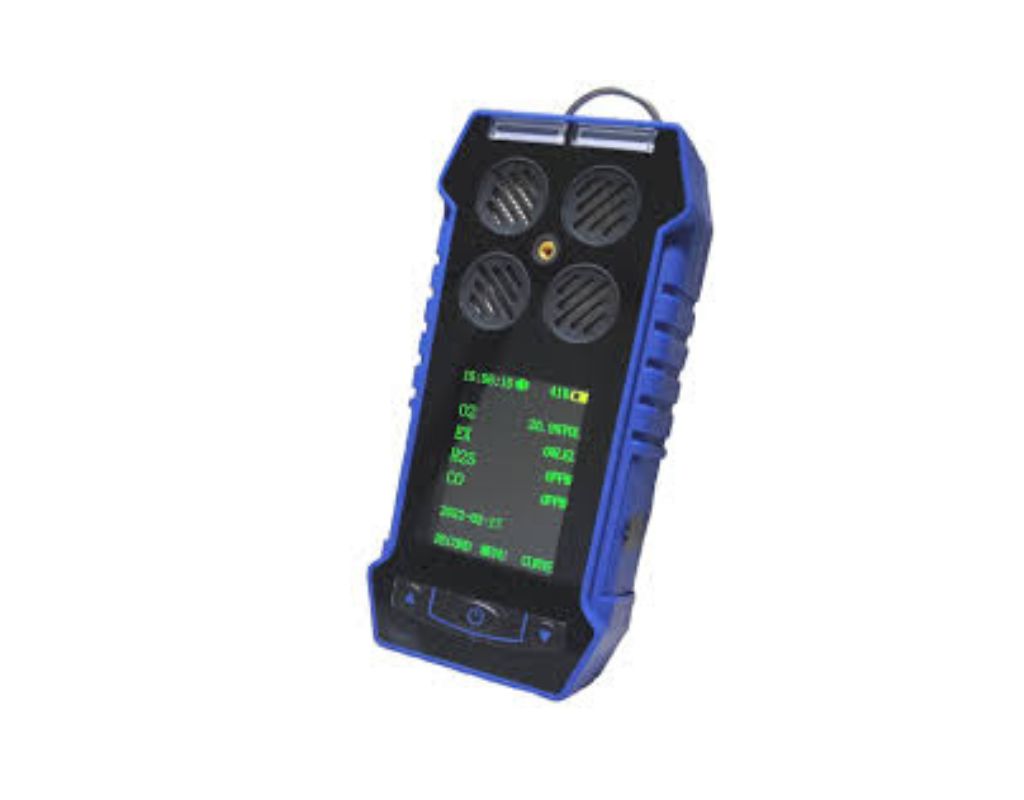
Gas Detector
A gas detector is a device designed to monitor the presence of specific gases in the surrounding environment. Gas detectors play a crucial role in air monitoring by providing early warnings of potentially harmful or hazardous gases. They are used in various industries, environments, and applications to ensure safety, maintain air quality, and prevent potential risks to human health and the environment.
Key aspects of gas detectors in air monitoring include
-
Gas Sensing Technology
Gas detectors use various sensing technologies to detect specific gases. Common technologies include electrochemical sensors, catalytic sensors, infrared sensors, and photoionization detectors.
-
Gas Detection Range
Different gas detectors are designed to detect specific gases or a range of gases. Some detectors are specialized for toxic gases, while others focus on combustible gases or oxygen levels.
-
Environmental Monitoring
Gas detectors are used in environmental monitoring to detect hazardous gases released from processes, leaks, or natural sources. This helps prevent environmental contamination.
-
Data Logging and Alarms
Many gas detectors have built-in data logging capabilities to record gas concentrations over time. They also feature alarms (audible, visual, or both) that activate when gas levels reach or exceed predefined thresholds.
-
Calibration and Maintenance
Regular calibration and maintenance are crucial to ensure accurate and reliable performance of gas detectors. Calibration ensures that the detector’s readings remain accurate over time.

Flow Meter
A flow meter is a device used to measure the rate of flow of a fluid or gas through a specific point in a system. In the context of air monitoring, flow meters are used to measure the rate at which air is moving through a particular space or duct. They play an important role in various applications, such as HVAC systems, industrial processes, environmental monitoring, and research.
Key points to consider about flow meters in air monitoring include
Types of Flow Meters:There are several types of flow meters used for air monitoring, including
-
Anemometers
These measure the speed of airflow and are commonly used in HVAC systems.
-
Pitot Tubes
These devices determine airspeed by measuring the difference between total pressure and static pressure in the airflow.
-
Vane Meters
Vane meters use a rotating vane placed in the airflow to measure flow rate.
-
Air Volume Measurement
Flow meters provide information about the volume of air passing through a specific point in a given time. This data is important for evaluating air circulation, ventilation rates, and HVAC system efficiency.
-
Environmental Monitoring
Flow meters are used in environmental monitoring to measure air movement in stacks, exhaust vents, and other areas to ensure compliance with emissions regulations.
-
Industrial Processes
In manufacturing and industrial settings, flow meters are used to monitor airflow rates in processes involving air handling, combustion, and exhaust.

Ambient Air Quality
Ambient air quality refers to the condition of the air in the outdoor environment, which includes the air we breathe in our everyday surroundings. Monitoring ambient air quality is crucial for assessing the levels of pollutants, gases, and particles present in the atmosphere and understanding their potential impact on human health, the environment, and overall quality of life.
Here are some key points about ambient air quality
-
Pollutants Monitored
Common pollutants monitored in ambient air quality include:
• Ozone (O3): A gas formed when pollutants from vehicles, industrial facilities, and other sources react with sunlight, leading to respiratory problems and other health effects.
• Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2): A gas released from combustion processes, especially from vehicles and industrial activities, with negative impacts on respiratory health.
• Sulfur Dioxide (SO2): Emitted from burning fossil fuels, it can cause respiratory and cardiovascular issues and contribute to acid rain.
• Carbon Monoxide (CO): A colorless, odorless gas produced by incomplete combustion, it can be harmful in high concentrations. -
Monitoring Stations
Ambient air quality is monitored through a network of monitoring stations located in urban, suburban, and rural areas. These stations collect data on pollutant concentrations, weather conditions, and other relevant factors.
-
Data Collection and Reporting
Monitoring stations continuously measure air quality parameters and transmit the data to central databases. This information is used to generate air quality indexes and reports that inform the public and policymakers.
-
Health Impacts
In manufacturing and industrial settings, flow meters are used to monitor airflow rates in processes involving air handling, combustion, and exhaust.
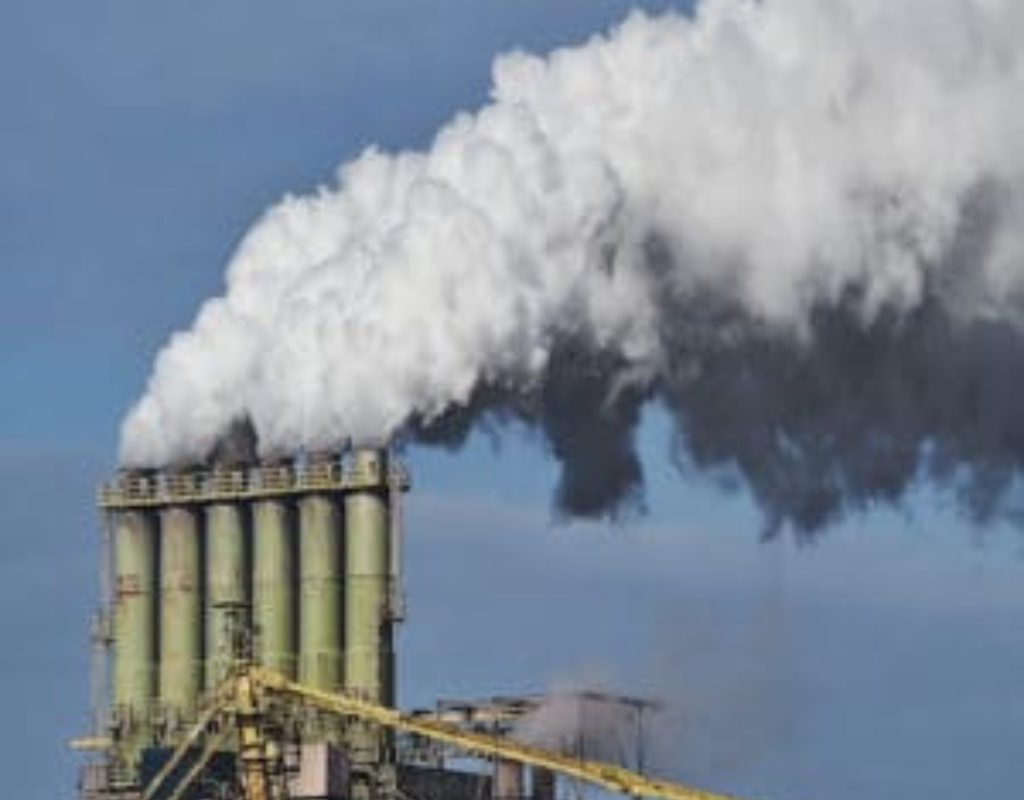

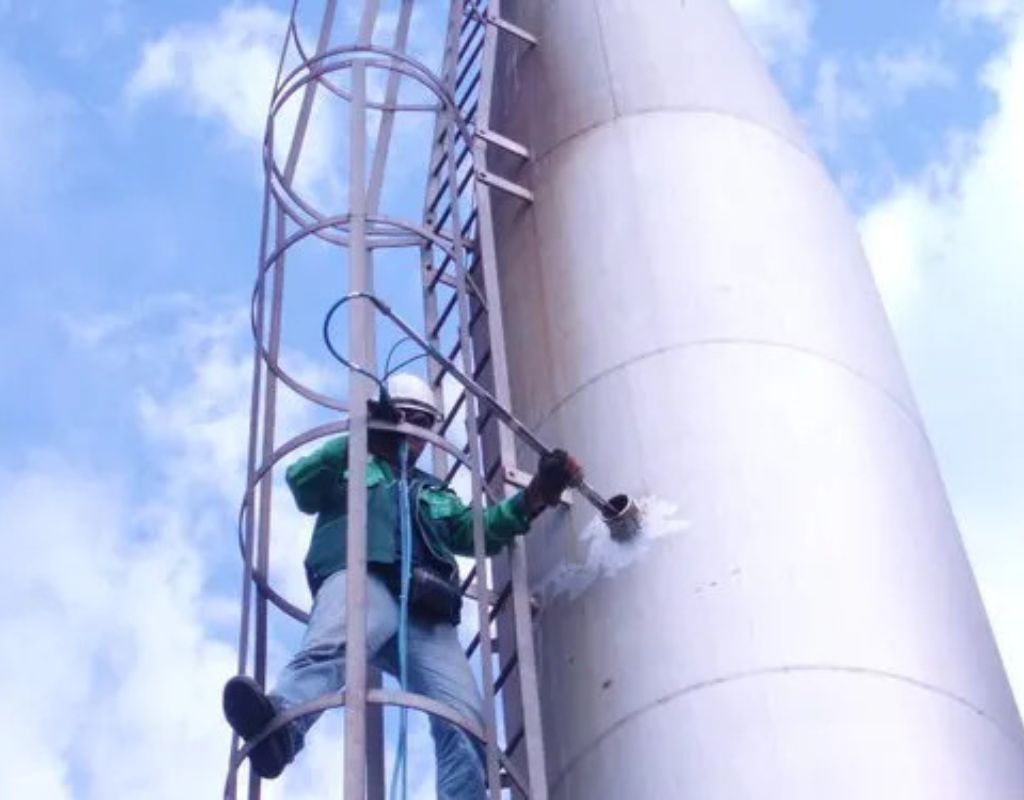
Stack Monitoring
Stack monitoring, also known as stack emissions monitoring or stack air quality monitoring, involves the measurement and analysis of pollutants released into the atmosphere from industrial stacks or chimneys. This monitoring is essential for assessing the environmental impact of industrial activities, ensuring compliance with air quality regulations, and identifying potential health and environmental risks associated with emissions.
Stack monitoring plays a crucial role in maintaining air quality, reducing pollution, and safeguarding public health and the environment. It ensures that industrial activities are conducted in a responsible and environmentally conscious manner while promoting sustainable development.

Fire Alarm Systems
Fire alarm systems and air monitoring systems serve distinct purposes, but they can interact in certain situations to enhance safety and response measures.
Here’s how fire alarm systems and air monitoring systems might intersect
-
Smoke Detection
Fire alarm systems often include smoke detectors that can sense the presence of smoke particles in the air. These detectors are crucial for early fire detection, allowing occupants to evacuate and responders to take action promptly. Air monitoring systems that measure particulate matter levels in the air can potentially detect higher-than-normal concentrations of smoke particles, which could trigger an alarm or alert in certain scenarios.
-
Air Quality Monitoring
In some cases, advanced fire alarm systems might incorporate air quality sensors as part of their monitoring capabilities. These sensors can detect elevated levels of gases like carbon monoxide (CO), which is often produced during fires. A sudden increase in CO levels could trigger an alarm or alert indicating the presence of a fire.
-
Fire Suppression Activation
Some fire alarm systems are linked to fire suppression systems, such as sprinklers. If a fire is detected, the fire alarm system can activate the appropriate suppression measures. Air monitoring systems could provide additional data to assess the severity of the situation and aid in deciding whether or not to activate suppression systems.
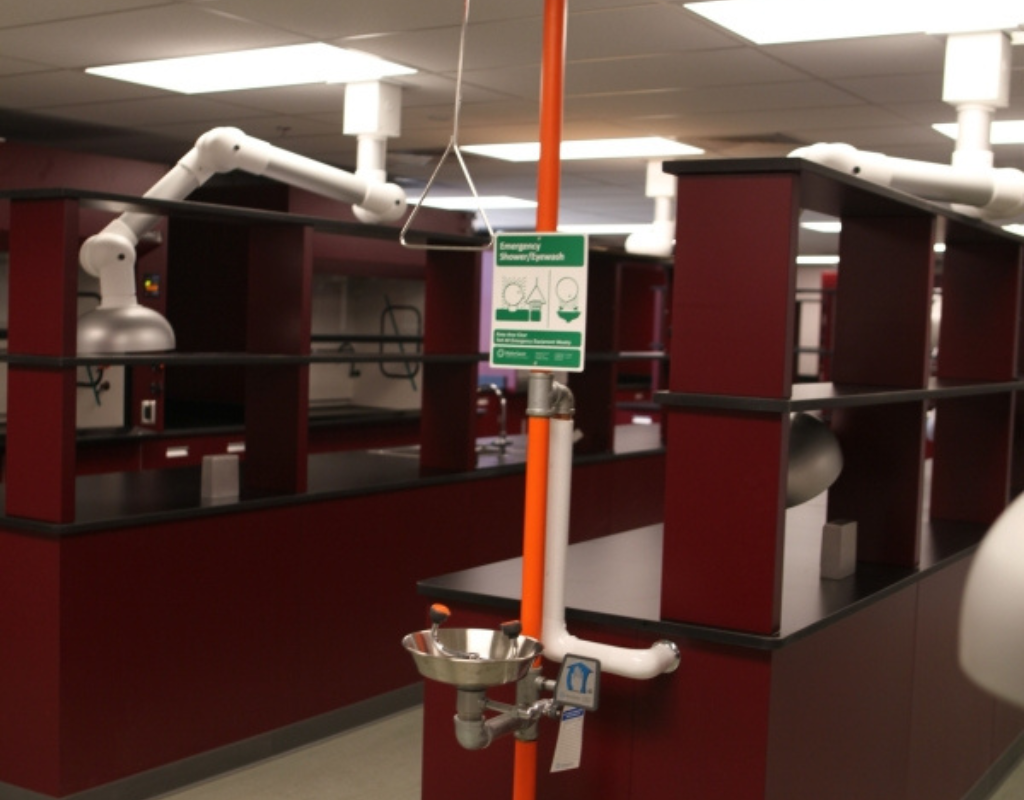
Industrial Shower
An industrial shower is a safety device commonly used in workplaces where employees are exposed to hazardous substances or materials that could potentially come into contact with their skin, eyes, or clothing. It’s important to clarify that industrial showers are not directly related to air monitoring, but they are crucial safety equipment in environments where workers are at risk of chemical splashes, spills, or contamination.
Key points about industrial showers include
-
Purpose
Industrial showers are designed to provide immediate decontamination in case of chemical spills, splashes, or other hazardous substance exposure. They help minimize the potential for injury or harm to workers.
-
Placement
Showers are typically located in areas where hazardous materials are handled, such as laboratories, manufacturing facilities, chemical plants, and research centers. They need to be easily accessible and reachable within seconds from areas where exposure could occur.
-
Water Temperature
Regulations often stipulate that the water temperature in industrial showers should be within a specific range, usually between 60-100°F (15-38°C), to prevent further harm to the skin.
-
Training
Workers need to be trained on how to use industrial showers and eyewash stations properly. Regular drills and awareness sessions ensure that employees know how to respond in case of an emergency.
-
Emergency Response Plan
Industrial showers are part of a comprehensive emergency response plan. This plan outlines the steps to take in case of chemical exposure, including activating the shower, notifying supervisors, seeking medical attention, and reporting the incident.

Join Us in Our Mission & Vision
Become a part of our journey to get relived from your problems, create experiences, achieve goals. Whether you're an individual looking for product/service or a business seeking product/service, we're here to make a difference together.
